Computer-based electrocardiographs and remote ECG analysis are a modern alternative to classical ECG machines and ECG analysis using printing.
ECG diagnostics current status
The majority of medical facilities is equipped with classical ECG machines providing the examination results using printing on thermal paper. The number of channels is determined by the thermal paper width (80 mm – 3 channels, 110 mm – 6 channels, 210 mm – 12 channels). The 3-channel and 6-channel models are most common.
As known, the standard electrocardiogram contains 12 leads. That is why the full ECG recording using a 3-channel machine is printed in 4 stages, and on a 6-channel one, it is printed in 2 stages. The best models of classic electrocardiographs can calculate ECG basic parameters, have a built-in memory enough to store several hundred electrocardiograms, and are equipped with LCD screens to display ECG and parameter tables.
However, doctors still write their medical comments based on printouts visually analyzing the ECG complexes. At the same time, modern methods of ECG computer analysis (heart rate variability analysis, cardiac arrhythmia analysis using long-term ECG recordings, vectorcardiography) cannot be used.
To read the electrocardiogram, it should be delivered to a doctor. If the doctor is not around, ECG analysis becomes a problem, especially in the case of emergency.
The ECG examination results are glued into the patient medical card. It takes a long time to find the necessary recordings in the medical card and compare them to each other. Besides, thermal paper printouts fade out with time and become unreadable. There is practically no way to integrate classical ECG machines with hospital information systems (HIS).
Computer-based electrocardiographs (using Easy ECG system, Russia, as an example)
A computer-based electrocardiograph (PC ECG) is a complex consisting of an ECG module and a computer with software installed for ECG recording, analyzing, storing, and transfer.
A computer-based electrocardiograph can use desktop PCs, laptops, and tablet PCs running Windows, Linux, or Android.
To record the patient’s ECG in ambulances, in hospital wards, or at home, mobile PC ECGs with an autonomous power supply based on tablet PCs are used. To conduct procedures in reception rooms or functional diagnostic rooms, PC ECGs are based on laptop or desktop PCs.
When compared to classical ECG machines, the main advantages of computer-based electrocardiographs are as follows:
- synchronous recording, displaying all 12 standard ECG leads;
- ECG recording duration from the standard 10 seconds to 60 minutes or more, allowing the arrhythmia and heart rate variability analyses;
- storing the results digitally in a database, the number of stored records is practically unlimited;
- automatic ECG medical conclusion;
- possibility to write a medical conclusion based on the examination results, saving it in the database together with the ECG recording;
- examination report printout using A4 format plain paper;
- possibility to send digital ECG recordings and examination protocols in PDF format via communication channels for remote ECG analysis;
- possibility to use the most modern methods to conduct remote computer ECG analysis;
- possibility to automatically add ECG examination results to the patient’s electronic medical record, integrating it with the HIS of the medical facility.
Computer-based electrocardiographs can be recommended to replace classic ECG devices everywhere – from the family doctor’s office to a large medical center.
Recording and remote ECG analysis systems based on PC ECGs
Computer-based electrocardiographs allow implementing the following principle: “ECG recording at the patient’s location, ECG analysis at the doctor’s location.”
When working in ambulances, mobile Internet is used to transfer ECG examination data to the analysis site while hospitals use a cable Internet or a local network (conventional or wireless).
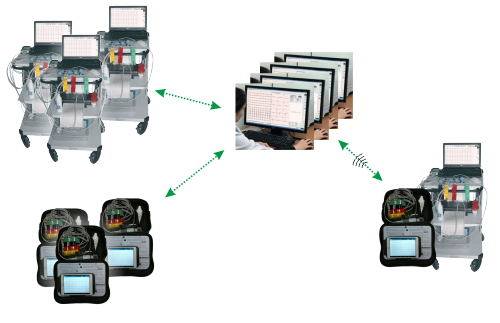
In large remote ECG analysis modular systems, two types of modules are distinguished: the central module where the ECG records are stored and the physician workplace where the results are analyzed.
In small systems, these two modules can be combined on one computer (for example, when the system is installed on the practicing cardiologist’s personal computer).
As a rule, a remote ECG system in a large hospital includes several physician workplaces operating concurrently. Such system composition is reliable and provides expansion possibilities like connecting additional physician workplaces when the flow of ECG records increases. Additional physician workplaces can be located outside the hospital if necessary. In these cases, the Web interface is utilized.
The patient and examination results database is stored in the central module of the system. In addition, using the module, communication with the hospital information system (HIS) is conducted.
The ECG analysis application installed on a PC at a physician workplace is a powerful tool.
The software features the standard possibilities like opening the newly received recording (as well as any other recording from the database), visualizing the ECG signal and its processed results, and writing a medical comment. The ECG signal and millimeter grid quality are higher on a display than on a traditional ECG printout. The application also allows:
- selecting a fragment of the signal to be analyzed, changing ECG filters, speed and sensitivity;
- changing, if necessary, the ECG wave markers position made by the application;
- inserting any fragments from an automatic medical conclusion and lines from a previously prepared template into the doctor’s medical comment;
- providing the possibility to compare different ECGs of the same patient;
- processing long ECG records to analyze arrhythmias, averaged complexes, and heart rate variability;
- performing ECG analysis in orthogonal leads and vectorcardiography both in true orthogonal leads and the interpolated one from a standard ECG;
- storing ECG examination protocols in a patient electronic medical record.
The transition from a traditional ECG diagnostic system to an ECG recording and remote ECG analysis system, based on PC ECGs, provides the following advantages:
- quick accessible qualified ECG examination for all patients, regardless of their location;
- medical staff reduction;
- reduced or no expenses previously necessary to purchase thermal paper;
- instant access to all patient’s ECG examination protocols for an attending physician using a patient electronic medical record.
When the transition to a new system is completed, it will result in lower morbidity and mortality caused by cardiovascular diseases.
13.04.2018